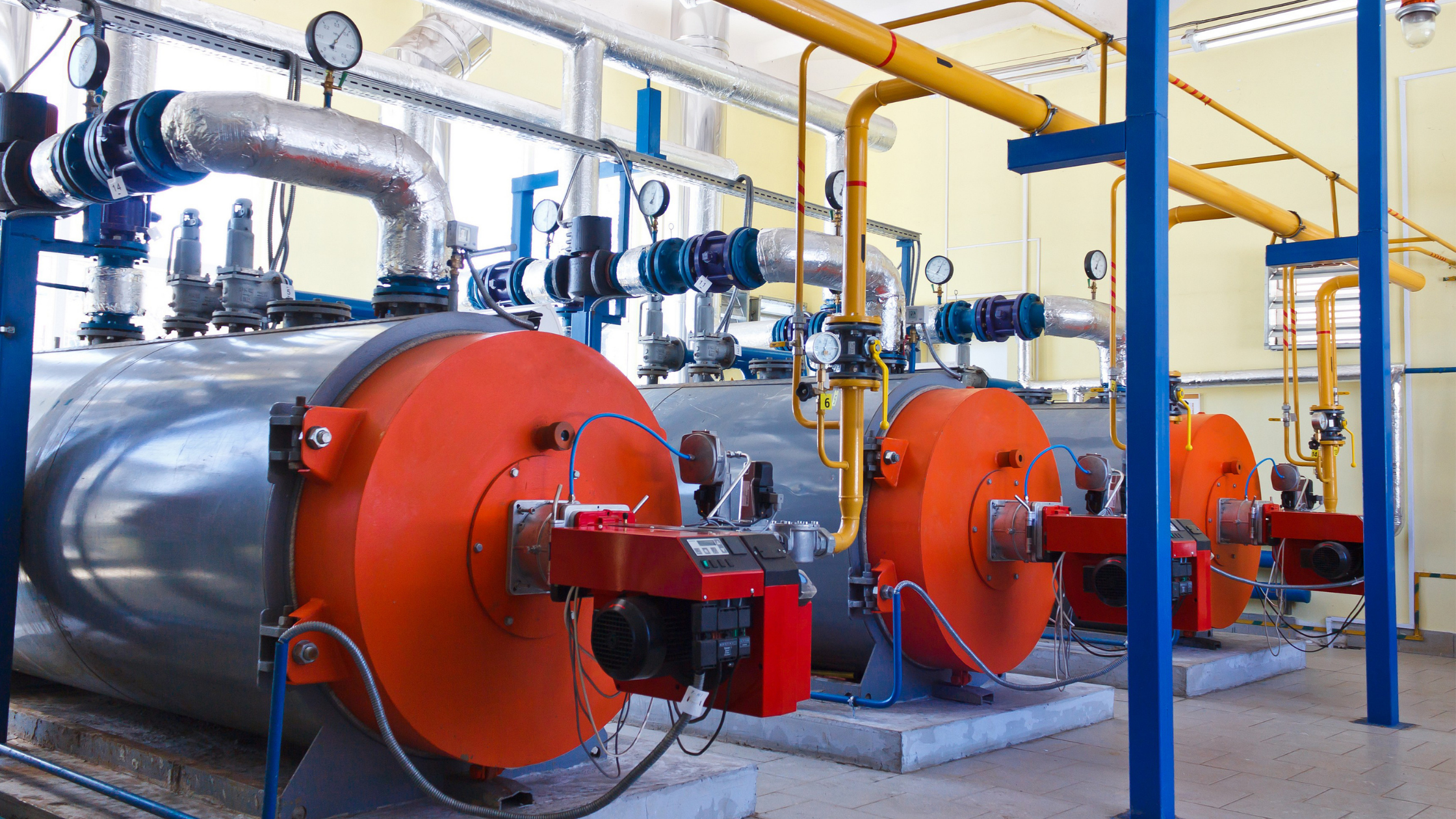
Industrial steam boilers are essential for a variety of applications, from generating power to processing in industries such as food, chemical, and manufacturing. Understanding their working principles, components, and design helps in efficient operation and maintenance.
What is an Industrial Steam Boiler?
An industrial steam boiler is a closed vessel that is designed to heat water to the boiling point in order to generate steam. The steam produced can then be used for various industrial processes like heating, sterilizing, driving turbines for electricity generation, or for powering machinery. The boiler itself operates by converting chemical energy (from fuel) or electrical energy into heat.
1. Working Principle of an Industrial Steam Boiler:-
-
Fuel Combustion: The boiler uses a fuel source (such as natural gas, coal, oil, or biomass) to create heat. The fuel is burned inside the combustion chamber where its energy is converted into heat.
-
Heat Transfer to Water: The heat from the combustion process is transferred to the water contained in the boiler’s heat exchanger or water tubes. This happens via thermal conduction. As the heat is absorbed, the water temperature rises and eventually reaches the boiling point, turning into steam.
-
Steam Production: Once the water reaches the boiling point, it begins to evaporate and form steam. The steam is then directed to the desired process area or steam header where it is used for industrial purposes.
-
Steam Pressure Control: The pressure of the steam is maintained through pressure control valves that ensure it remains within safe operating limits. The steam may be stored in a steam drum for distribution or further use.
-
Condensation (Optional): Once the steam has done its job, it is cooled and condensed back into water in the condensation system. This water can either be discarded or sent back to the boiler to be reheated, forming a closed-loop system for energy efficiency.
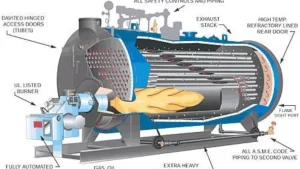
2. Key Components of an Industrial Steam Boiler:-
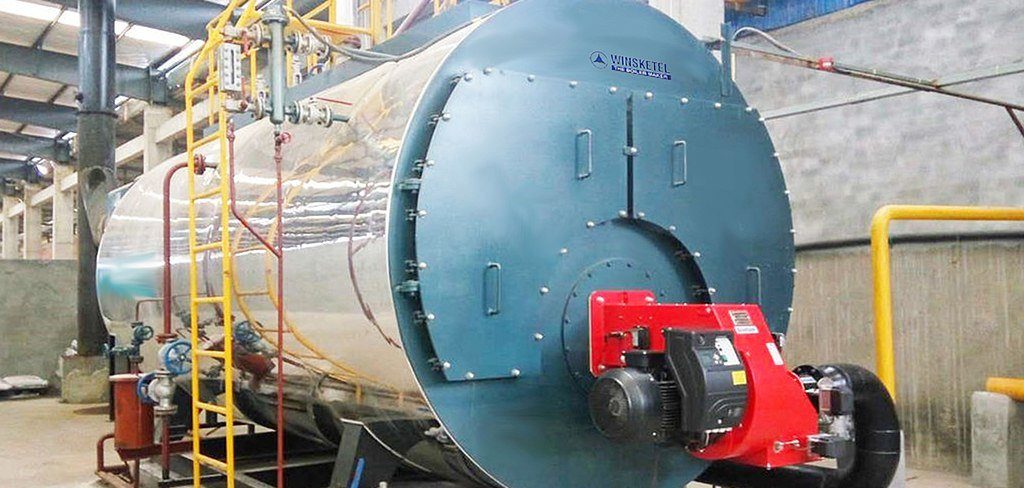
- Furnace/Combustion Chamber: Where fuel combustion occurs. The heat from the furnace is transferred to the water.
- Burner: Responsible for mixing fuel and air to produce an efficient flame for combustion.
- Water Drum/Steam Drum: This holds water and steam within the boiler and separates steam from water.
- Economizer: A heat exchanger that preheats the boiler feedwater using the flue gases, improving efficiency.
- Superheater: Adds additional heat to the steam after it leaves the steam drum, increasing its energy content.
- Air Preheater: Warms the incoming air using the flue gases, further enhancing combustion efficiency.
- Feed Pump: Pumps water into the boiler at high pressure.
- Safety Valves: Ensure the boiler operates safely by releasing excess pressure.
- Steam Output Valve: Controls the release of steam to industrial applications.
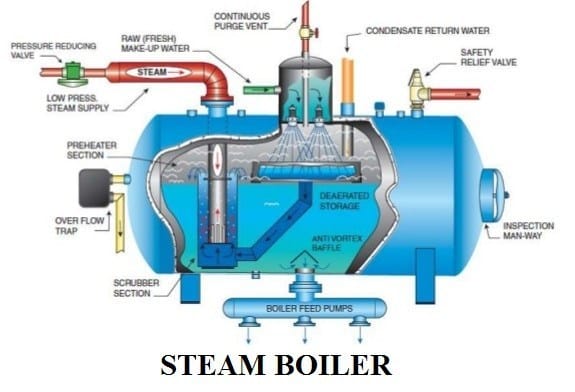
3. Industrial Steam Boiler Diagram
A simplified industrial boiler diagram usually includes:
- Combustion Chamber: Where fuel is burned.
- Burner: Positioned to feed fuel-air mix to the chamber.
- Water and Steam Drum: Holds water and steam for heating.
- Economizer and Air Preheater: Components that recycle heat from flue gases.
- Superheater: Produces high-temperature, high-pressure steam.
- Safety Valves and Steam Output Valve: Safety controls and output release.
The diagram typically illustrates how fuel combustion produces heat, which is transferred through tubes to water, generating steam for use.
Why is Understanding the Boiler Important?
For any further queries, please let us know! we’ll be happy to assist you with any questions or provide additional information you may need. Contact us@ 07053901803